
Insects on Our Plates: The Future of Sustainable Food Systems
In a world grappling with food insecurity, climate change, and rapid population growth, traditional food sources are under immense pressure. The Global Atlas of Edible Insects: Analysis of Diversity and Commonality Contributing to Food Systems and Sustainability provides invaluable insights into how edible insects can revolutionize our food systems and offers solutions to some of the pressing global food challenges.
Yes, insects.
Edible Insects: A Nutritious and Sustainable Option
Edible insects, with their low environmental footprint, high nutritional values, and efficient growth rates, emerge as champions in sustainable food production. The study documents an astonishing variety of 2205 insect species consumed across 128 countries, with significant representation in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. Countries like Mexico and Thailand lead in insect consumption, highlighting a deep-rooted cultural acceptance and a growing awareness of sustainability needs.
Global Distribution and Consumption Patterns
The study’s analysis shows a diverse global distribution of edible insects. Predominant in this list are Coleoptera (beetles), Hymenoptera (bees, wasps, ants), Lepidoptera (butterflies, moths), and Orthoptera (grasshoppers, crickets). Notably, Asia boasts the highest number of edible insects, significantly influencing dietary choices across the continent. (see the figure from the study below)
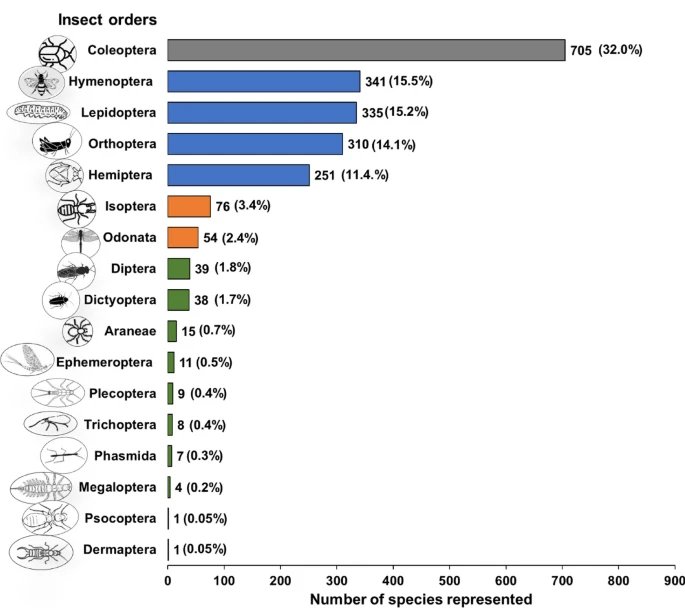
The Role in Public Health
For public health practitioners, the implications of this research are manifold. Edible insects offer an array of essential nutrients, potentially addressing deficiencies in protein and other vital nutrients in regions plagued by food insecurity. Countries with high insect consumption, interestingly, do not always correlate with food insecurity levels, suggesting that cultural acceptance plays a crucial role in dietary choices.
Challenges and Opportunities
The acceptance of edible insects in Western countries remains low, but the tide is turning with growing environmental consciousness. Public health initiatives could leverage this shift, promoting insects as nutritious and eco-friendly food alternatives. However, overcoming the stigma and cultural barriers remains a significant challenge.
Policy and Future Research
Policy makers must focus on creating frameworks that encourage the cultivation and consumption of edible insects. Investing in research to understand the ecological impact, nutritional value, and best farming practices for edible insects will be crucial in making them a mainstay in global food systems.
Conclusion
The “Global Atlas of Edible Insects” offers a comprehensive view of the potential role of edible insects in global food sustainability. As we confront the limitations of traditional agriculture, insects emerge not just as a food source, but as a beacon of hope for a more sustainable and nutritious future. Public health practitioners have a pivotal role to play in integrating this knowledge into policies and practices that shape the future of our food systems.
Lead the Way in Public Health – Get Your Weekly Insight!
Ready to lead the charge in health advocacy and research? ‘This Week in Public Health’ delivers essential weekly updates, keeping you informed and ahead in the dynamic field of public health. With insights on the latest breakthroughs and initiatives, our newsletter is your gateway to being a proactive leader. Subscribe for free and start shaping the future of public health today!



